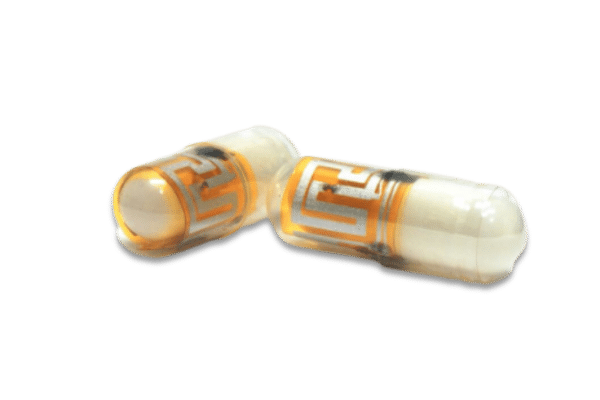
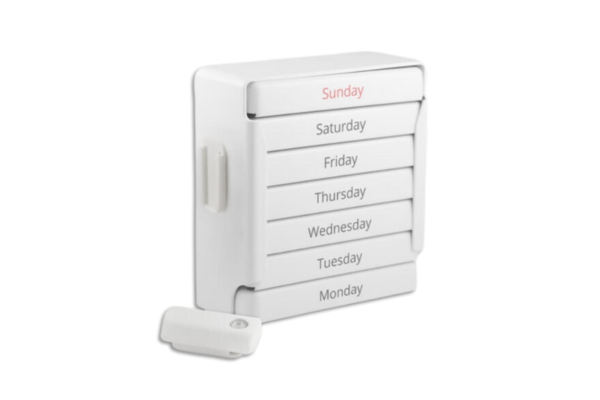
Yes – it is generally welcomed by trial participants, although acceptance may vary depending on the study population and the specific type of packing play a part. From an acceptability standpoint, selected packaging should be easy to use and not place burden on participants.
One of the reasons why digital packaging is generally well-accepted is that it can provide patients with additional support and tools to help them adhere to their medication regimen. For example, regardless of the packaging or device the participant is using, AARDEX Group’s mobile app, MEMS® Mobile can provide participants with reminders to take their medication, which can be particularly helpful for patients who have difficulty remembering to take their medication on time.
Digital packaging can also provide patients with real-time feedback on their medication-taking behaviors, which can help them stay on track with their medication regimen. This can be particularly helpful for patients who are struggling with adherence-related issues or who are taking complex medication regimens.
In addition, digital packaging can provide patients with a sense of control over their medication regimen. By being able to track their medication-taking behavior and receive feedback on their adherence, patients may feel more empowered and engaged in their healthcare.